Many people don’t know that resting metabolism affects daily calorie burn, even at rest. You can boost your resting metabolism with simple strategies. This helps your body burn more calories without much effort. This guide offers seven easy tips. These tips can help boost your metabolism, raise your energy, and manage your weight. Get science-based tips to boost your metabolism every day.

Table of Contents
- I. Understanding Resting Metabolism
- II. Types of Metabolism
- III. Common factors that affect metabolism
- IV. Step-by-Step Guide to Boosting Resting Metabolism
- V. Tip #1: Build More Muscle Mass
- VI. Tip #2: Eat enough protein every day
- VII. Tip #3: Stay hydrated
- VIII. Tip #4: Get Quality Sleep
- IX. Tip #5: Drink green tea or coffee
- X. Tip #6: Manage Stress Levels
- XI. Tip #7: Avoid Skipping Meals
- XII. Pros and Cons of Natural Metabolism-Boosting Strategies
- XIII. Creating a long-term metabolism-boosting lifestyle
- 7 Proven Ways to Boost Your Resting Metabolism
- FAQ
Key Takeaways:
Doing regular strength training and high-intensity interval workouts can boost your resting metabolism. This helps your body burn more calories, even when you’re not active.
Eating protein-rich meals and staying hydrated help maintain muscle and support metabolism. Together, these factors boost your resting metabolic rate.
Getting good sleep and managing stress help balance hormones. This supports the body’s ability to burn calories while resting.
I. Understanding Resting Metabolism
Your resting metabolism is the energy your body uses to keep vital functions going while at rest. This process accounts for a significant part of your daily calorie expenditure. Understanding how resting metabolism works helps you make better choices. You can boost your resting metabolism and burn more calories, even when you’re not exercising.
1.1. Definition of Resting Metabolism
Resting metabolism is the energy your body needs for basic functions. These include breathing, circulation, and cell production. This happens while you’re awake but resting. It shows the basic number of calories you burn each day without extra exercise. This is the starting point for your total energy use.
1.2. The Importance of Resting Metabolism

Resting metabolism is key to managing your energy balance. Knowing how many calories you burn at rest can help you improve your diet and lifestyle. This leads to better results. Boosting your resting metabolism helps you manage weight and improve health.
Understanding resting metabolism clarifies the reasons some people burn calories with ease. Muscle mass, age, and hormone levels affect how well your body uses energy at rest. Boosting your resting metabolism helps you maintain a healthy weight. It also supports good metabolic health in the long run.
1.3. Key Factors Influencing Resting Metabolism
Key factors affect your resting metabolism. These factors influence how many calories your body burns when you’re at rest. These include:
-
Muscle mass – more lean muscle increases calorie burn.
-
Age – metabolism tends to slow down as you get older.
-
Hormonal balance – certain hormones regulate energy expenditure.
-
Genetics – your metabolic rate is partly inherited.
-
Body size and composition – larger bodies usually need more energy.
This knowledge helps you find areas to improve your resting metabolism. You can then burn more calories in a more efficient way.
Influencing your resting metabolism is possible by focusing on factors such as:
-
Increasing lean muscle through strength training.
-
Balancing hormones with proper nutrition and sleep.
-
Managing body composition through consistent physical activity.
This method lets you take steps to boost your metabolism. It also helps you burn more calories.
II. Types of Metabolism
Metabolism includes all chemical processes in your body. It has different types that affect how many calories you burn each day. Understanding these can help you achieve a large increase in your resting metabolism. Key types include:
To boost your metabolism, focus on certain exercises and nutrition.
| Type of Metabolism | Description |
|---|---|
| Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) | Energy used at complete rest for vital functions |
| Resting Metabolism | Energy burned at rest but slightly higher than BMR |
| Active Metabolism | Calories burned through physical activity |
| Thermic Effect of Food (TEF) | Energy used to digest and process food |
| Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) | The sum of all calories burned in a day |
You can optimize your metabolism by targeting specific types with tailored activities and nutrition.
2.1. Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
BMR, or basal metabolic rate, is the number of calories your body needs at complete rest. It keeps vital functions going, like breathing, circulation, and cell production. This rate shows the least energy your body needs. It means you burn these calories even when you’re resting or asleep. Knowing your BMR helps you set realistic goals to boost your resting metabolism.
2.2. Resting Metabolism vs. Active Metabolism

Basal metabolism measures the energy your body uses at rest. Active metabolism refers to the calories you burn during physical activities. This includes walking, running, or intense workouts. Both types add to your total calorie burn. But resting metabolism makes up the biggest part of daily energy use. Enhancing your resting metabolism helps you burn more calories even when inactive.
Resting metabolism covers energy for basic body functions. In contrast, active metabolism changes a lot based on how active you are. Boost your resting metabolism by building muscle or improving cellular efficiency. This helps you burn more calories even when at rest.
2.3. Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE)
Expenditure includes BMR, active metabolism, and the thermic effect of food. Together, they show how many calories you burn daily. Knowing your TDEE is key for creating nutrition and exercise plans. It helps boost your resting metabolism and manage your weight through efficient strategies.
Calculating TDEE helps you change your calorie intake. You can create a deficit to lose weight or a surplus to gain muscle. Boost your resting metabolism. These strategies affect BMR and active components. This change raises your TDEE, improving metabolic health and energy balance.
III. Common factors that affect metabolism
Now that you know how metabolism works in your body, let’s look at the main factors that affect it. These include:
-
Age and Gender
-
Body Composition
-
Hormonal Influences
-
Genetics
-
Physical Activity Levels
How these elements work together affects how well you burn calories at rest. This gives you ideas on how to improve your resting metabolism.
3.1. Age and Gender

As you age, your metabolism changes. This often leads to a lower resting metabolic rate. Men often burn calories at a faster rate. This is due to having more muscle mass and different hormones. In contrast, women often have a slower resting metabolism. Knowing these factors helps you adjust your strategies. This way, you can boost your resting metabolism as your body goes through key changes.
3.2. Body Composition
Body composition plays a significant role in how many calories you burn at rest. More lean muscle means a higher resting metabolic rate. This is because muscle needs more energy to maintain than fat. Building muscle helps increase your resting metabolism. It’s a great way to boost your metabolism.
Lean muscle is active tissue, so your body burns energy all the time, even when you’re still. Building muscle through strength training boosts your calorie burn. This change in body composition helps improve your resting metabolism over time.
3.3. Hormonal Influences
Hormones control many metabolic processes. If they’re imbalanced, they can slow down or speed up your metabolism. Thyroid hormones boost your metabolic rate. Insulin and cortisol levels also affect how well your body uses energy. To boost your resting metabolism, managing hormonal health is crucial.
Thyroid function, stress hormones, and sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone can impact your metabolism. Talk to a healthcare provider about hormonal disruptions. They can help you find personalized ways to boost your metabolism and energy levels.
IV. Step-by-Step Guide to Boosting Resting Metabolism
To boost your resting metabolism, start with a clear plan. First, understand your current level. Then, set achievable goals. Finally, create a realistic approach that suits your lifestyle.
This guide will help you.
-
Assess your metabolic rate.
-
Set motivating goals.
-
Build habits that boost calorie burn over time.
Using structured assessments and clear strategies helps boost your resting metabolism. This approach is efficient and safe.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Assess Your Current Metabolic Rate |
| 2 | Set Realistic and Personalized Goals |
| 3 | Create a Sustainable Action Plan |
4.1. Assessing Your Current Metabolic Rate
Your metabolic rate shows how many calories you burn while resting. It’s key for creating plans to boost your metabolism. For accurate assessment, use tools like indirect calorimetry or metabolic rate calculators. These tools consider your age, weight, height, and activity level. Finding this baseline helps you track progress. You can change your approach to boost your resting metabolism with greater effectiveness.
4.2. Setting Realistic Goals

When setting goals, focus on targets you can achieve. Make sure they fit your lifestyle and health. Unrealistic expectations can cause frustration or burnout. Clear, manageable milestones encourage steady progress. They also help you stay motivated over time. These goals should focus on gradual improvements in metabolic rate and healthy habits.
Break larger goals into smaller, clear steps. For example, focus on increasing muscle mass, improving diet, or adding daily activity. You can celebrate your wins and stay motivated. This helps boost your resting metabolism.
4.3. Creating a Sustainable Action Plan
To boost your metabolism, create an easy action plan. Make sure it fits into your daily routine and helps you stick with it long-term. This means finding the right mix of exercise, food, rest, and stress relief. It should fit your personal likes and daily routine. Your plan should be flexible. It needs to change as you discover what helps your metabolism the most.
Combine different activities like strength training and aerobic exercise. This can boost your resting metabolism without stressing your body too much. Adjusting your plan helps keep progress steady. It also boosts calorie burning.
The 200 Most Popular EBooks>>>
V. Tip #1: Build More Muscle Mass
Building more muscle mass is a great way to boost your resting metabolism. Muscle tissue burns more calories than fat, even when you’re resting. So, having more muscle increases your baseline calorie burn. Adding resistance training to your routine will help you gain muscle. It will also improve your strength and body composition. Focusing on muscle development gives you a metabolic edge. This helps with burning calories and managing weight over time.
5.1. Benefits of Muscle Over Fat
Muscle is active tissue. It needs more energy to maintain than fat does. This means your body burns more calories around the clock even when you’re not exercising. Muscle does more than raise your resting metabolic rate. It also improves insulin sensitivity, boosts physical performance, and helps with posture. Building more muscle boosts your body’s efficiency. It also helps prevent metabolic slowdown as you age. So, adding muscle is a smart way to increase your resting metabolism.
5.2. Recommended Exercises for Muscle Gain
To build muscle and boost your metabolism, focus on compound exercises. These workouts target large muscle groups. Exercises like squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and rows work many muscles at once. This helps boost muscle growth and burn more calories. Using progressive overload is crucial. This means increasing weights or resistance in small increments. It helps muscles adapt and boosts metabolism over time.
Muscle gains happen when you push your body with resistance exercises. These exercises stress your muscles more than you usually experience. Using free weights, resistance bands, or bodyweight exercises can help. Push-ups and lunges are great options. They boost muscle use and improve coordination. High-intensity strength training sessions boost your post-exercise oxygen consumption. This means you keep burning calories even after your workout. So, your resting metabolism gets an extra boost.
5.3. Tips for Incorporating Strength Training
Here are some tips to help you include strength training in your routine. This will boost your resting metabolism:
-
Start with two to three sessions per week, targeting major muscle groups.
-
Use proper form and technique to avoid injury.
-
Increase weights or resistance over time to challenge your muscles.
-
Combine strength training with enough protein intake for muscle repair.
This method helps you make steady progress with less risk. So, it becomes easier to build muscle and boost your metabolism over time.
Strength training can boost your daily routine. It helps you stay consistent and get better results.
-
Schedule workouts at convenient times to create a habit.
-
Mix different exercises to avoid plateaus and boredom.
-
Use online or in-person coaching for guidance and motivation.
-
Track your progress to stay motivated and focused.
This strategy helps you keep building muscle. This speeds up your metabolism and helps you raise your resting metabolism over time.
VI. Tip #2: Eat enough protein every day
To boost your resting metabolism, make sure you eat enough protein. Eating enough protein each day helps build and repair muscles. It also boosts your metabolism because it takes more energy to digest protein. Focusing on protein helps your body burn more calories, even at rest. This supports weight management and boosts your metabolic health.
6.1. Role of Protein in Metabolism

A small boost in protein intake can raise your resting metabolism. This happens because protein burns more calories during digestion than fats or carbs. Your body uses more energy to break down protein. This leads to burning more calories. Protein helps maintain muscle. This is important because muscle burns more calories than fat. So, it can boost your metabolic rate over time.
6.2. Best Sources of Protein
Protein comes from many sources. Eating a variety helps you meet your nutritional needs. Lean meats, fish, eggs, and dairy are excellent options. Legumes and plant-based proteins, like quinoa and tofu, are also great choices. They suit various diets and lifestyles.
Balancing animal and plant-based proteins is key. This way, you get all the amino acids and nutrients you need. Mixing different protein sources helps create sustainable eating habits. It also boosts your metabolism, so you burn more calories even when resting.
6.3. Daily Protein Intake Recommendations
Consuming enough protein daily can significantly boost your resting metabolism. Aim for 1.2 to 2.0 grams of protein for every kilogram of your body weight. This depends on how active you are and what your goals are. These tips help maintain muscle mass and enhance the metabolic benefits of protein.
Recommendations vary based on factors like age, physical activity, and metabolic health. Adjust your protein intake to support your metabolism and well-being. Talking to a nutrition expert can help you find the right protein amount for your needs.
VII. Tip #3: Stay hydrated
Drinking enough water is easy. It can lead to a much greater increase in your resting metabolism. Drinking enough water helps your body work well. It even boosts calorie burning when you’re resting. When you don’t stay hydrated, your metabolism can slow down. This makes it tougher for your body to process energy well. By maintaining hydration, you’re supporting your metabolism’s natural processes.
7.1. Importance of Hydration
Water is essential for every metabolic reaction in your body. It plays a key role in these processes. Staying hydrated helps your cells work well. It creates the right conditions for them to turn nutrients into energy. Proper fluid levels help regulate temperature and transport nutrients. This is crucial for keeping metabolism efficient all day long.
7.2. How Hydration Affects Metabolism
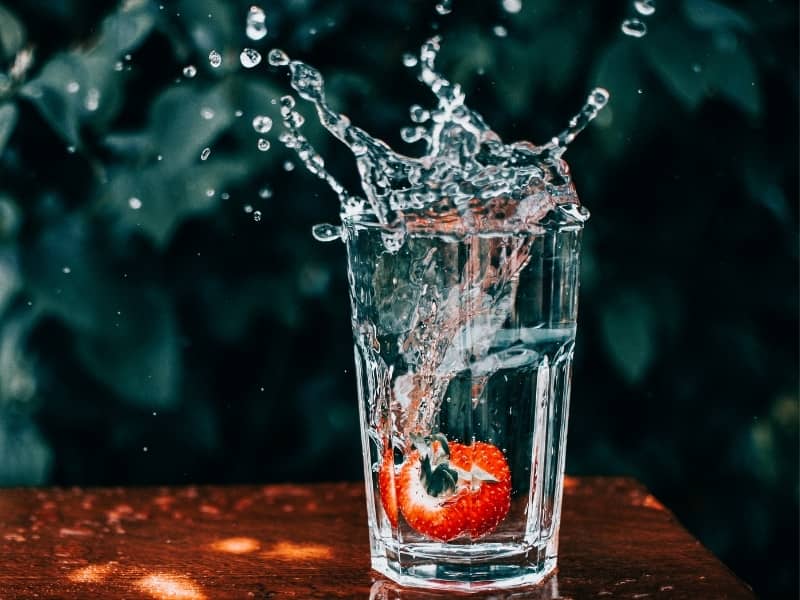

Even mild dehydration can slow your metabolism. When your body lacks water, it conserves energy. Drinking water can boost your resting energy expenditure. This means your body burns more calories after you hydrate. Water-induced thermogenesis demonstrates the direct impact of hydration on your metabolic rate.
Also, drinking enough water helps your organs. This is important for your kidneys and liver. They need hydration to detoxify and break down nutrients in the proper way. This efficient processing helps your body get the most energy from food. This leads to a higher resting metabolic rate. Staying hydrated helps prevent fatigue. This keeps you active and lets you burn more calories.
7.3. Hydration Tips for Optimal Metabolism
Optimal hydration strategies can help you keep your metabolic rate elevated. Consider these practical tips to boost your resting metabolism through hydration:
-
Drink at least 8 glasses (about 2 liters) of water daily.
-
Start your day with a glass of water to kick-start your metabolism.
-
Include hydrating foods, like fruits and vegetables, in your diet.
-
Carry a water bottle as a reminder to sip water at regular intervals.
-
Avoid sugary drinks that may impair metabolic efficiency.
Noticing when your body is thirsty is key to staying hydrated all day.
Another step to enhancing hydration includes timing your fluid intake around meals. Drinking water before meals helps your metabolism. It improves digestion and helps with portion control. Also, check the color of your urine. It can show how hydrated you are. Aim for light yellow to clear for better metabolic function. Using apps or reminders may support consistent hydration habits. Noticing these signals helps you change your fluid intake to match your body’s needs.
VIII. Tip #4: Get Quality Sleep
Lack of quality sleep can slow your metabolism. This makes it tougher to burn calories in an efficient manner. When you don’t get enough sleep, your body has a hard time managing hormones. These hormones help control hunger and energy use. Getting good sleep helps keep your metabolism in check. This means you burn more calories, even when you’re resting. Good sleep helps your body recover. It also controls appetite and supports metabolism.
8.1. Sleep’s Impact on Metabolism

Disrupting your sleep can hurt your metabolism. It changes hormone levels like leptin and ghrelin. These hormones control hunger and fullness. Lack of sleep lowers your resting metabolic rate. This means you burn fewer calories daily. Inadequate sleep also lowers insulin sensitivity. This raises the risk of weight gain and metabolic disorders. Consistent, quality sleep supports a healthy metabolism. It helps your body burn calories in an effective manner.
8.2. Tips for Improving Sleep Quality
Small changes to your bedtime routine can improve your sleep quality. Better sleep can also boost your resting metabolism. Practice these habits regularly to create an environment that promotes restful sleep.
-
Keep a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time each day.
-
Limit exposure to screens and blue light at least an hour before bedtime.
-
Create a relaxing pre-sleep ritual, such as reading or meditating.
-
Ensure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet.
-
Avoid caffeine and heavy meals close to bedtime.
Improving your sleep quality can boost your metabolic health. This change can help you burn more calories.
Metabolism depends on the healing processes happening during uninterrupted deep sleep. Good sleep habits help you fall asleep faster. They also improve the quality of your sleep. This boosts the time you spend in deep REM sleep. During this phase, your body repairs tissues and regulates hormones with efficiency. Also, using relaxation techniques to manage stress before bed can help reduce interruptions. This way, your metabolism can work better while you sleep. Improving your sleep space and habits will help boost your resting metabolism.
8.3. The Link Between Sleep and Weight Management
Some studies show a link between bad sleep and a higher risk of weight gain and obesity. Not getting enough quality sleep messes with your hunger hormones. This can cause you to overeat and crave high-calorie foods. Additionally, sleep deprivation reduces your motivation for physical activity, further hampering calorie expenditure. Getting enough sleep helps you maintain a healthy weight. It supports your metabolism and controls your appetite.
Also, getting more and better sleep helps burn fat and boosts energy metabolism all day. This means your body uses stored fat better for energy. This helps with weight management. Getting enough sleep lowers stress. High stress can lead to emotional eating and an upset metabolism. Focusing on quality rest helps you build a strong base for weight control. It also boosts your resting metabolism.
IX. Tip #5: Drink green tea or coffee
Green tea and coffee are different from many drinks. They have natural compounds that can boost your resting metabolism. This means you burn more calories, even when you’re not moving. Adding these drinks to your daily routine can boost your metabolism. Their special bioactive ingredients help increase energy use and fat burning. Drinking green tea or coffee can give your metabolism a boost. This can help you manage your weight, but remember to enjoy them in moderation.
9.1. Metabolism-Boosting Compounds in Caffeine
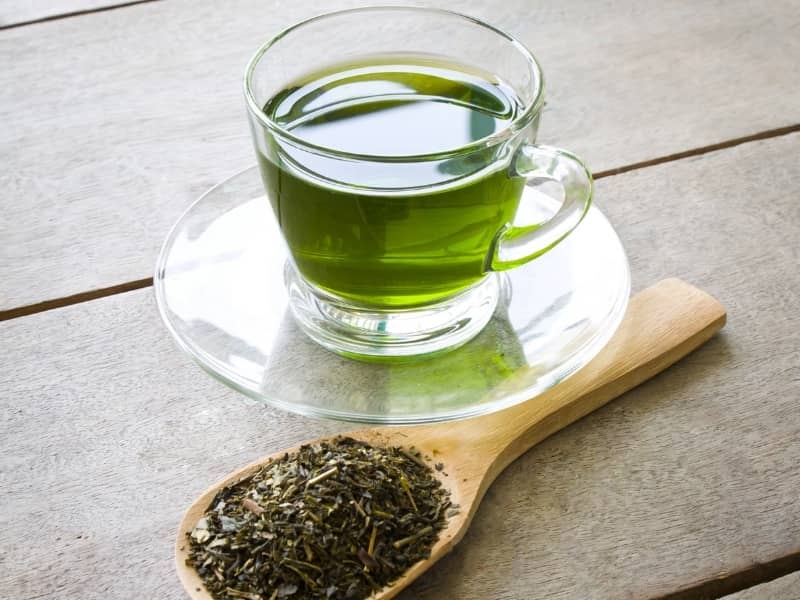

Green tea and coffee boost your metabolism due to the caffeine they contain. Caffeine is a natural stimulant. Caffeine increases your metabolic rate by promoting thermogenesis and enhancing fat oxidation. This means your body uses more calories even when you’re resting because of caffeine. Caffeine can also enhance focus and energy. This boost helps you stay active and raises your resting metabolism.
9.2. Health Benefits of Green Tea
Green tea has a special mix of antioxidants and catechins. One key component is epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). This blend offers health benefits that go beyond boosting metabolism. These compounds boost your resting calorie burn. They also support heart health, lower inflammation, and improve insulin sensitivity. Drinking green tea often can speed up your metabolism. It also helps keep you healthy over time.
Compounds in green tea, like polyphenols and EGCG, are well-studied. They have positive effects on metabolic function. These substances can help lower fat absorption. They also increase calorie burn. Together, they boost your resting metabolism. Green tea is a great choice for metabolism and health. Its antioxidants protect cells from oxidative stress. This stress can harm metabolic health.
9.3. Recommended Consumption Levels
To boost your metabolism, drink green tea or coffee in moderation. Drinking three to four cups of green tea or one to two cups of coffee each day gives you a good amount of caffeine. Plus, it comes with health benefits. This helps prevent issues like jitteriness or trouble sleeping. Balancing your intake ensures you enjoy metabolic benefits while maintaining well-being.
Caffeine and antioxidants change based on how you prepare them and how much you serve. So, pay attention to how your body reacts. Drinking green tea in the morning or early afternoon boosts your metabolism. It won’t affect your sleep. Staying within the recommended limits helps maintain a healthy metabolism. It also prevents tolerance buildup, which can reduce these benefits over time.
X. Tip #6: Manage Stress Levels
Even if you eat well and exercise, stress can hurt your resting metabolism. Stress triggers hormonal changes that slow down metabolic processes and promote fat storage. Managing stress helps your body burn calories better and boosts metabolic health. Try adding stress management techniques to your routine. They can help boost your metabolism, even during tough times.
10.1. The Effect of Stress on Metabolism
Stress makes your body release cortisol. This hormone can reduce your resting metabolic rate. It can also increase your cravings for high-calorie foods. High cortisol levels make your body save energy and store fat, especially in the belly. This hormonal change throws off your metabolism’s balance. As a result, it becomes tougher to maintain or lose weight when you’re stressed.
10.2. Effective Stress-Reduction Techniques

To lower stress, try these practices: mindfulness meditation, deep breathing, and regular exercise. These methods help control your nervous system. They also lower cortisol levels and boost mental clarity. Using these techniques daily helps calm your mind. It also boosts your metabolism, so you burn calories even when you’re resting.
10 minutes of deep breathing each day can lower your heart rate and cut cortisol levels. Moderate aerobic exercise, like walking or yoga, helps lower stress. It also boosts your metabolism. Mindfulness meditation helps you focus and reduce anxiety. This, in turn, supports your metabolism and helps burn calories.
10.3. How Stress Management Supports Weight Goals
Stress management is key for many people to reach and maintain their weight goals. Controlling stress helps you avoid metabolic slowdown. It also keeps you from emotional eating, which can mess up your calorie control. A stable emotional state helps your body work well. This means you burn calories better, both day and night.
Managing stress well helps you maintain healthy habits. These habits can boost your resting metabolism. Minimizing stress hormones helps your body work better. This supports fat loss and keeps your muscles. Mental well-being and physical metabolism work together. This connection is key to lasting success in managing your weight.
XI. Tip #7: Avoid Skipping Meals
To boost your resting metabolism, give your body fuel often. Skipping meals can throw off your metabolism. This causes your body to store energy instead of using calories efficiently. Keeping regular meal times helps your metabolism stay steady. This way, you burn more calories all day and don’t feel deprived or sluggish.
11.1. The Consequences of Skipping Meals
Many people think skipping meals helps with weight loss. But this often backfires and slows down your metabolism. Skipping meals makes your body think there’s not enough energy. So, it goes into conservation mode and burns fewer calories while at rest. This response can make you feel hungrier later. It may lead to overeating, which makes it harder to boost your resting metabolism.
11.2. How Regular Meals Support Metabolism

Consuming meals at consistent intervals helps maintain a high metabolism. Consuming meals at consistent intervals supports your digestion and facilitates calorie burning. We call this the thermic effect of food. Avoiding long gaps between meals helps keep your metabolism active. This also supports steady energy levels.
Consistent eating helps balance hormones that control metabolism. This includes insulin and leptin. Balanced hormone changes help your body use energy better and store less fat. This boosts your resting metabolic rate and aids in weight management.
11.3. Meal Frequency Recommendations
Most people have different needs. Still, it’s best to eat three balanced meals and one or two healthy snacks each day. This helps keep your metabolism up. This approach stops excessive hunger. It stabilizes blood sugar and keeps your energy steady. All this helps you burn calories better, even when you’re at rest.
The quality of these meals holds equal importance. Adding protein, fiber, and healthy fats to your meals can boost your metabolism. These nutrients help you feel full and increase the thermic effect of food. This means you get extra benefits as you work to improve your resting metabolism.
XII. Pros and Cons of Natural Metabolism-Boosting Strategies
To enhance your resting metabolism through natural methods, weigh the advantages and disadvantages. Natural methods can boost your calorie-burning power without drugs. But not every approach works for everyone. The table below shows important pros and cons. It helps you make a decision that fits your health and lifestyle.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Improves daily calorie expenditure | Results can be gradual, requiring patience |
| Supports overall health with lifestyle changes | Certain strategies may lead to fatigue if overdone |
| Reduces risk of metabolic diseases | Some methods require time and consistency |
| Enhances energy levels and physical performance | May require dietary adjustments you find challenging |
| Accessible without prescription or costly supplements | Underlying medical conditions may limit effectiveness |
| Can improve mood and mental well-being | Potential for improper technique or misinformation |
| Encourages healthy long-term habits | Inconsistent application reduces benefits |
| Flexibility to combine multiple strategies | Time commitment might not fit busy schedules |
| Often promotes better sleep patterns | Some interventions may cause mild discomfort or soreness |
| Non-invasive and low risk when done correctly | Lack of immediate visible changes can lower motivation |
12.1. Pros of Increasing Resting Metabolism
Boosting your resting metabolism increases your daily calorie burn. This helps with weight management and improves your vitality. Improved metabolism helps your body use energy with greater efficiency. This can lead to improved workout performance and more stamina during the day. Also, these natural strategies encourage healthier habits. They lead to more exercise and better nutrition. This helps your heart and mind stay healthy over time.
12.2. Potential Cons and Considerations
Cons include that boosting your metabolism naturally requires significant effort and patience. Changes usually occur over a long period. You may feel tired or sore if you exercise too much or don’t rest enough. Changing your diet to boost your metabolism may seem tough at first. Health conditions can affect how well metabolism-boosting methods work. So, it’s important to pay attention to your body and adjust your strategies as needed.
Resting metabolism differs from person to person. Genetics, age, and health can affect it. Increasing your metabolism is important, but you must watch how your body reacts. This way, you can prevent burnout or other negative effects. Doing too much or using the wrong methods can cause problems. For example, excessive exercise or sudden diet changes may lead to issues. You might end up with nutrient deficiencies or extra stress. Close attention to your body’s feedback and moderation is key for sustainable progress.
12.3. Weighing the Benefits Against Risks
Weigh the benefits of boosting your resting metabolism against the downsides. Doing so can lead to better calorie burning and improved well-being. Different methods can help. Strength training, protein-rich diets, and getting enough sleep boost benefits and cut downsides. Your approach should match your lifestyle, preferences, and health. This way, you can achieve lasting success.
Considering these factors helps you create metabolism-boosting strategies. These strategies improve your energy use while keeping your health intact. Take small steps, watch for changes, and stay flexible. This helps you use the benefits well and reduce the downsides. Using natural methods helps you boost your metabolism in a way that avoids risks. You can enjoy more calories without extra risks. This way, reaching a higher resting metabolic rate is both safe and rewarding.
XIII. Creating a long-term metabolism-boosting lifestyle
To boost your resting metabolism for the long term, a lifestyle change is key. Instead of looking for quick fixes, focus on habits that boost your metabolism over time. Include healthy eating, exercise, good sleep, and stress relief in your daily routine. This lifestyle change helps you burn more calories, even when you’re resting. It supports lasting weight management and better health.
13.1. Establishing Healthy Habits
To boost your resting metabolism, start by building healthy habits. Make them second nature. Balanced meals with protein, regular activity, and enough sleep boost your metabolism. Making simple routines helps these positive habits last. This builds a strong base to boost your metabolic rate for the long term.
13.2. Monitoring Progress
Some tracking is necessary to understand how well your metabolism-boosting strategies work. Monitoring your energy, body composition, and resting metabolic rate shows your progress. You can use tools or get expert help for this. This feedback helps keep you motivated. It also lets you make smart choices. This way, you can support a higher calorie burn while at rest.
Keeping track of your workouts and meals is helpful. Frequent checks of your weight and muscle mass also provide important insights. You can spot trends like more muscle helping your metabolism or plateaus that signal it’s time for a change. Wearable tech and metabolic testing give you exact data to improve your plan.
13.3. Adjusting Your Plan

Lifestyle changes that boost your resting metabolism need regular evaluation and change. As your body adapts, what once worked might lose effectiveness. You need to adjust your diet, exercise, or sleep to keep boosting your metabolism. Flexibility and responsiveness in your plan ensure continuous progress and prevent stagnation.
Set regular checkpoints. This helps you know when to boost exercise, add new foods for metabolism, or improve sleep habits. This adaptive mindset makes your metabolism-boosting journey dynamic. It turns a routine into an active process that maximizes calorie burn over time.
7 Proven Ways to Boost Your Resting Metabolism
You’ve looked at the strategies. Now, you know how to boost your resting metabolism and burn more calories. You can boost your calorie-burning potential by using different methods. Try strength training. Eat more protein. Drink plenty of water. Also, get good sleep. These methods help you control your metabolism. They boost energy use and support your health. Sticking to these principles will help you get lasting results. Your metabolism can become a strong ally in your wellness journey.
FAQ
Q1: What is resting metabolism, and why is it important for burning calories?
Resting metabolism is the energy your body uses when at rest. It keeps vital functions going, like breathing, circulation, and cell production. It accounts for a significant part of your total daily calorie expenditure. Boosting your resting metabolism helps you burn more calories daily. This can aid in managing weight and improving your energy levels.
Q2: How does muscle mass influence resting metabolic rate?
Muscle tissue burns more calories than fat tissue, even when you’re resting. Building muscle with strength training can help increase your resting metabolism. Your body will use more energy during the day. This helps you burn more calories, even when you’re not exercising.
Q3: Can diet affect resting metabolism, and if so, how?
Yes, diet has a significant impact on resting metabolism. Eating enough protein can boost the thermic effect of food. This is the energy needed to digest and process nutrients. Some foods and drinks, such as green tea and spicy dishes, can provide a small increase in metabolism. Eating regular, balanced meals keeps blood sugar and energy levels steady. This supports a healthy metabolism.
Q4: Does sleep quality influence resting metabolism? How much sleep do we need?
Sleep quality and duration play a vital role in regulating resting metabolism. Poor sleep can mess with hormones that manage hunger and energy use. This may slow down metabolism. Most adults need 7 to 9 hours of good sleep each night. This helps keep their metabolism and health in top shape.
Q5: How does hydration affect resting metabolism and calorie burning?
Maintaining proper hydration is important to support metabolic processes. Many cellular functions, including those related to energy production, involve water. Drinking water can provide a short-term increase in your resting metabolism. This happens through a process called water-induced thermogenesis. Drinking cold water might boost this effect. The body uses energy to heat the water to its normal temperature.
The 200 Most Popular EBooks>>>
Last Updated on August 2, 2025 by Holistic Healths






